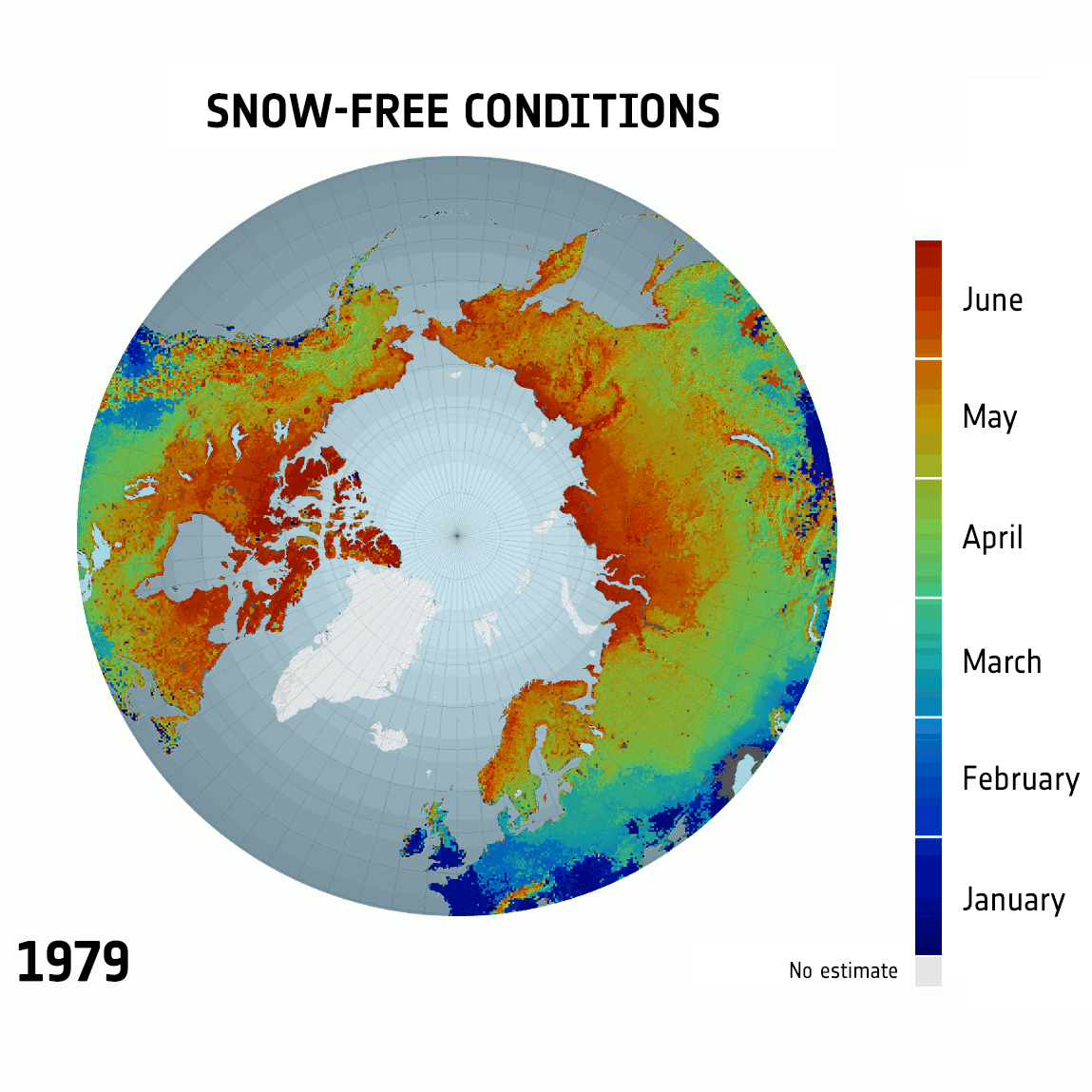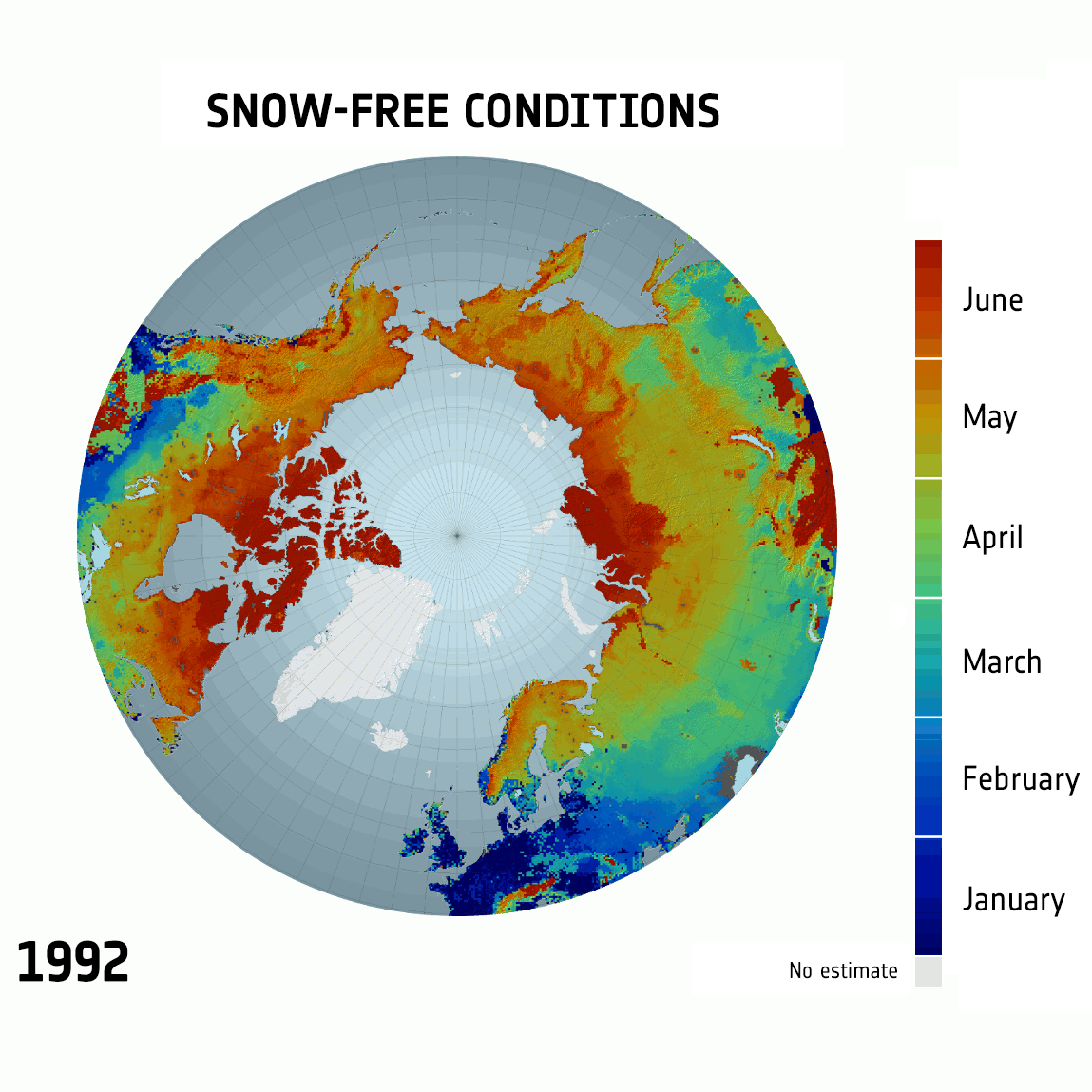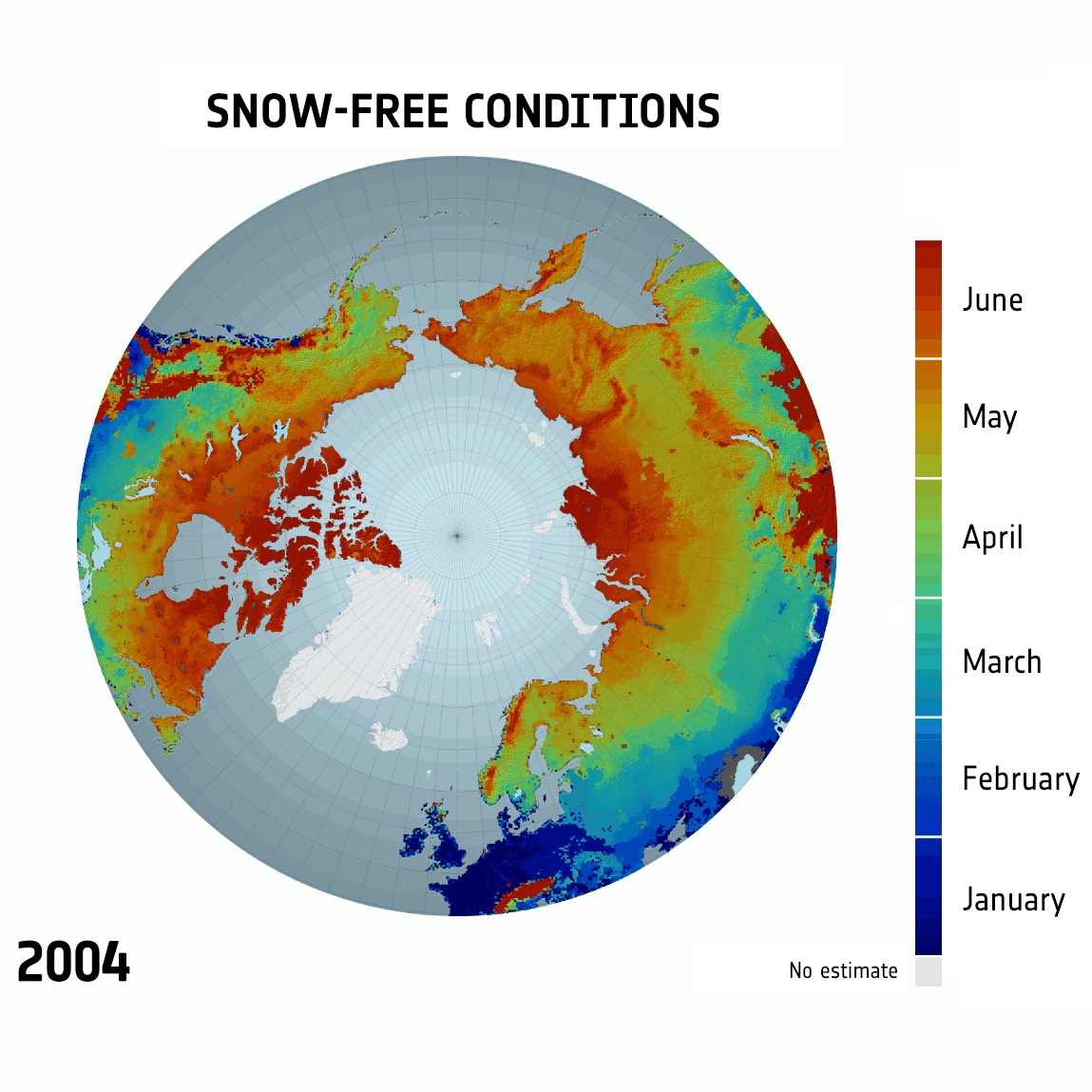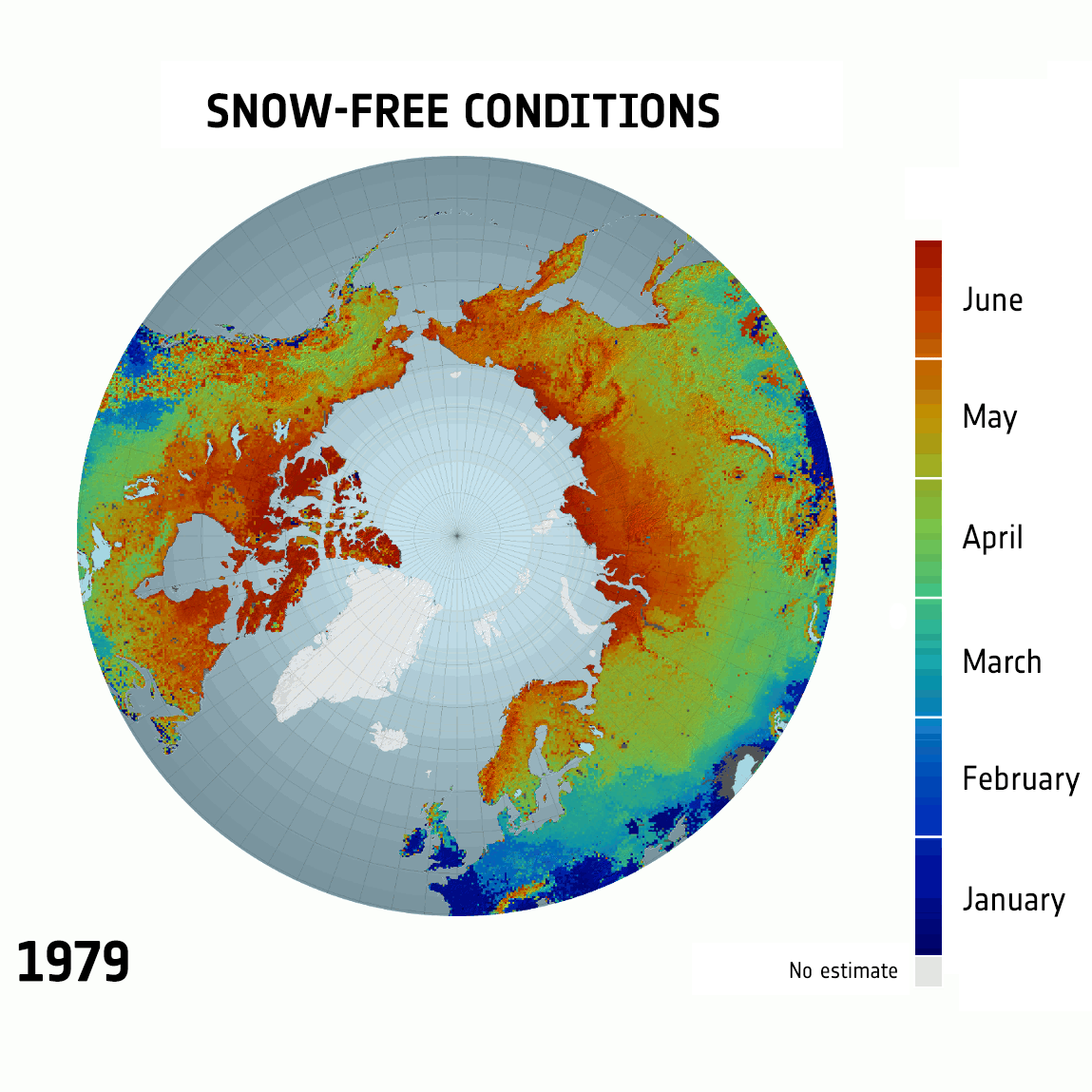
West Antarctic Ice Sheet Stable?
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: Exceeding critical temperature limits in the Southern Ocean may cause the collapse of West Antarctic Ice Sheets.
A sharp rise in sea levels From the ALFRED WEGENER INSTITUTE, HELMHOLTZ CENTRE FOR POLAR AND MARINE RESEARCH and modeled certainty department: Future warming of the Southern Ocean caused by rising greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere may severely…"
Exceeding critical temperature limits in the Southern Ocean may cause the collapse of West Antarctic Ice Sheets and a sharp rise in sea levels From the ALFRED WEGENER INSTITUTE, HELMHOLTZ CENTRE FOR POLAR AND MARINE RESEARCH and modeled certainty department: Future warming of the Southern Ocean caused by rising greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere may severely…
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: West Antarctic Ice Sheet Exceeding critical temperature limits in the Southern Ocean may cause the collapse of ice sheets and a sharp rise in sea levels.
arctic Ice Sheet stable: From the ALFRED WEGENER INSTITUTE, HELMHOLTZ CENTRE FOR POLAR AND MARINE RESEARCH and modeled certainty department:
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: Future warming of the Southern Ocean caused by rising greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere may severely disrupt the stability of the West
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: The Antarctic and Greenland are covered by West Antarctic Ice Sheets, which together store more than two thirds of the world’s freshwater. As temperatures rise, ice masses melt; in consequence the global sea level rises and threatens the coastal regions.
According to scientific findings, the Antarctic already today contributes to the annual sea level rise with 0.4 millimetres.
However, the most recent world climate assessment report (IPCC 2013) pointed out that the development of the ice masses in the Antarctic is not yet sufficiently understood.
Climate modellers of the Alfred Wegener Institute have therefore analysed the changes to the West Antarctic Ice Sheet in the last interglacial period and applied their findings to future projections.
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: “Both, for the last interglacial period around 125,000 years ago and for the future our study identifies critical temperature limits in the Southern Ocean: If the ocean temperature rises by more than two degrees Celsius compared with today, the marine-based West Antarctic Ice Sheet will be irreversibly lost.
This will then lead to a significant Antarctic contribution to the sea level rise of some three to five metres”, explains AWI climate scientist Johannes Sutter.
This rise, however, will only occur if climate change continues as it has up to now.
The researchers make these assessments based on model simulations.
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: “Given a business-as-usual scenario of global warming, the collapse of the West Antarctic could proceed very rapidly and the West Antarctic ice masses could completely disappear within the next 1,000 years”, says Johannes Sutter, the study’s main author, who has just completed his doctoral thesis on this topic.
“The core objective of the study is to understand the dynamics of the West Antarctic during the last interglacial period and the associated rise in sea level.
It has been a mystery until now how the estimated sea level rise of a total of about seven metres came about during the last interglacial period.
Because other studies indicate that Greenland alone could not have done it”, Prof Gerrit Lohmann, the head of the research project, adds.
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: The new findings on the dynamics of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet allow conclusions to be drawn about how the West Antarctic Ice Sheet might behave in the wake of global warming.
According to model calculations, the ice masses shrink in two phases.
The first phase leads to a retreat of the ice shelves, ice masses that float on the ocean in the coastal area of the Antarctic stabilising the major glacier systems of the West Antarctic.
If the ice shelves are lost, the ice masses and glaciers of the hinterland accelerate and the ice flow into the oceans increases.
As a result, the sea level rises, the grounding line retreats, leading to a further floatation of the grounded ice masses with a progressing acceleration and retreat of the glaciers.
These will achieve a stable intermediate state only once – put simply – a mountain ridge under the ice temporarily slows down the retreat of the ice masses.
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: If the ocean temperature continues to rise or if the grounding line of the inland ice reaches a steeply ascending subsurface, then the glaciers will continue to retreat even if the initial stable intermediate state has been reached.
Ultimately, this leads to a complete collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
“Two maxima are also apparent in the reconstructions of the sea level rise in the last interglacial period.
The behaviour of the West Antarctic in our newly developed model could be the mechanistic explanation for this”, says a delighted Johannes Sutter.
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: The climate scientists used two models in their study.
A climate model that includes various Earth system components such as atmosphere, oceans and vegetation, and a dynamic West Antarctic Ice Sheet model that includes all basic components of an West Antarctic Ice Sheet (floating ice shelves, grounded inland ice on the subsurface, the movement of the grounding line).
Two different simulations were used with the climate model for the last interglacial period to feed the West Antarctic Ice Sheet model with all the necessary climate information.
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: “One reason for the considerable uncertainties when it comes to projecting the development of the sea level is that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet does not simply rest on the continent in steady state, but rather can be subject to dramatic changes”, according to the AWI climate scientists, emphasizing the challenges involved in making good estimates.
“Some feedback processes, such as between the ice shelf areas and the ocean underneath, have not yet been incorporated into the climate models.
We at the AWI as well as other international groups are working on this full steam.”
Improving our understanding of the systematic interaction between climate and West Antarctic Ice Sheets is crucial in order to answer one of the central questions of current climate research and for future generations: How steeply and, above all, how quickly can the sea level rise in the future?
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: The result would be a rise in the global sea level by several meters.
A collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet may have occurred during the last interglacial period 125,000 years ago, a period when the polar surface temperature was around two degrees Celsius higher than today.
Is West Antarctic Ice Sheet stable: This is the result of a series of model simulations which the researchers of the Alfred Wegener Institute Helmholtz Center for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) have published on-line in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.




